Visibility Analysis¶
Visibility analysis estimates which buildings or areas are visible from a given observer point (or set of points) within a specific distance. This is useful in assessing visual accessibility, urban form, and perceptual exposure in public space.
The module supports multiple modes of analysis:
Accurate Method¶
Computes visibility using fine-grained raster-based methods. More accurate for local areas, but slower.
objectnat.get_visibility_accurate(point_from, obstacles, view_distance, return_max_view_dist=False)
¶Function to get accurate visibility from a given point to buildings within a given distance.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
point_from
|
Point | GeoDataFrame
|
The point or GeoDataFrame with 1 point from which the line of sight is drawn. If Point is provided it should be in the same crs as obstacles. |
required |
obstacles
|
GeoDataFrame
|
A GeoDataFrame containing the geometry of the obstacles. |
required |
view_distance
|
float
|
The distance of view from the point. |
required |
return_max_view_dist
|
bool
|
If True, the max view distance is returned with view polygon in tuple. |
False
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
Polygon | GeoDataFrame | tuple[Polygon | GeoDataFrame, float]
|
A polygon representing the area of visibility from the given point or polygon with max view distance. if point_from was a GeoDataFrame, return GeoDataFrame with one feature, else Polygon. |
Notes
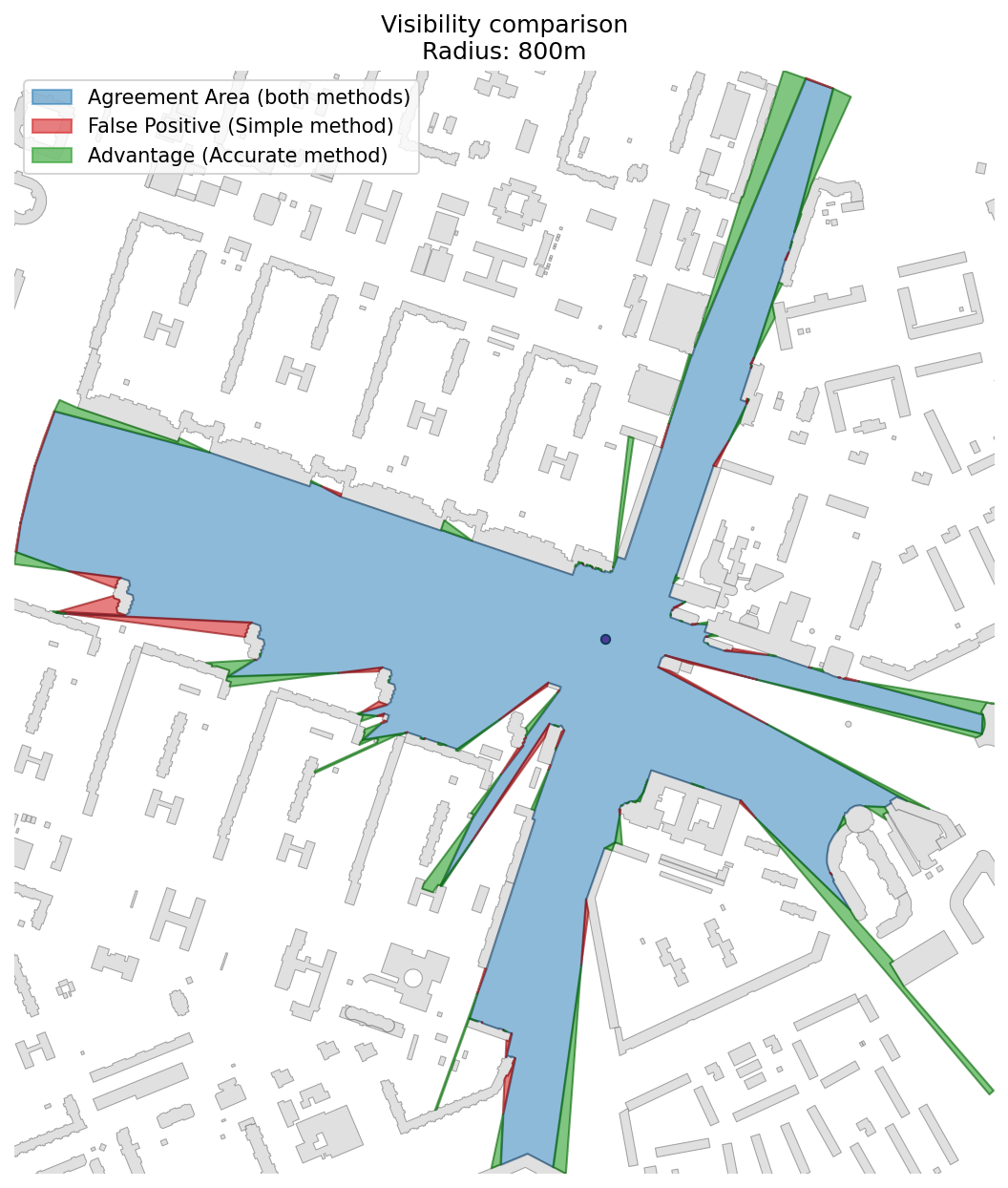
If a quick result is important, consider using the get_visibility() function instead.
However, please note that get_visibility() may provide less accurate results.
Source code in src\objectnat\methods\visibility\visibility_analysis.py
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 | |
Fast Approximate Method¶
Optimized for large datasets or large areas. Uses geometry simplifications and vector-based visibility.
objectnat.get_visibility(point_from, obstacles, view_distance, resolution=32)
¶Function to get a quick estimate of visibility from a given point to buildings within a given distance.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
point_from
|
Point | GeoDataFrame
|
The point or GeoDataFrame with 1 point from which the line of sight is drawn. If Point is provided it should be in the same crs as obstacles. |
required |
obstacles
|
GeoDataFrame
|
A GeoDataFrame containing the geometry of the buildings. |
required |
view_distance
|
float
|
The distance of view from the point. |
required |
resolution
|
int)
|
Buffer resolution for more accuracy (may give result slower) |
32
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
Polygon | GeoDataFrame
|
A polygon representing the area of visibility from the given point. if point_from was a GeoDataFrame, return GeoDataFrame with one feature, else Polygon. |
Notes
This function provides a quicker but less accurate result compared to get_visibility_accurate().
If accuracy is important, consider using get_visibility_accurate() instead.
Source code in src\objectnat\methods\visibility\visibility_analysis.py
162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 | |
Catchment Visibility from Multiple Points¶
Performs visibility analysis for a dense grid of observer points.
Used to generate catchment areas of visibility (e.g., “where can this building be seen from?”).
objectnat.get_visibilities_from_points(points, obstacles, view_distance, sectors_n=None, max_workers=cpu_count())
¶Calculate visibility polygons from a set of points considering obstacles within a specified view distance.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
points
|
GeoDataFrame
|
GeoDataFrame containing the points from which visibility is calculated. |
required |
obstacles
|
GeoDataFrame
|
GeoDataFrame containing the obstacles that block visibility. |
required |
view_distance
|
int
|
The maximum distance from each point within which visibility is calculated. |
required |
sectors_n
|
int
|
Number of sectors to divide the view into for more detailed visibility calculations. Defaults to None. |
None
|
max_workers
|
int
|
Maximum workers in multiproccesing, multipocessing.cpu_count() by default. |
cpu_count()
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
list[Polygon]
|
A list of visibility polygons for each input point. |
Notes
This function uses get_visibility_accurate() in multiprocessing way.
Source code in src\objectnat\methods\visibility\visibility_analysis.py
232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 | |
The image below shows an example of using visibility polygons to calculate "visibility pools" - areas in an urban environment that are most visible from different locations.